In today’s competitive business landscape, efficiency and organization are paramount. Managing various departments, data streams, and resources can quickly become overwhelming, hindering growth and profitability. This is where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems come into play. ERP software acts as a central hub, integrating core business processes into a unified platform, streamlining operations and boosting overall performance.
What is an ERP Program?

An ERP program is a comprehensive software suite designed to manage and automate critical business functions across an entire organization. Think of it as the central nervous system of your company, connecting departments like finance, accounting, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, and sales. Each department utilizes specific modules within the ERP system, fostering collaboration and information sharing.
Core functionalities of an ERP System
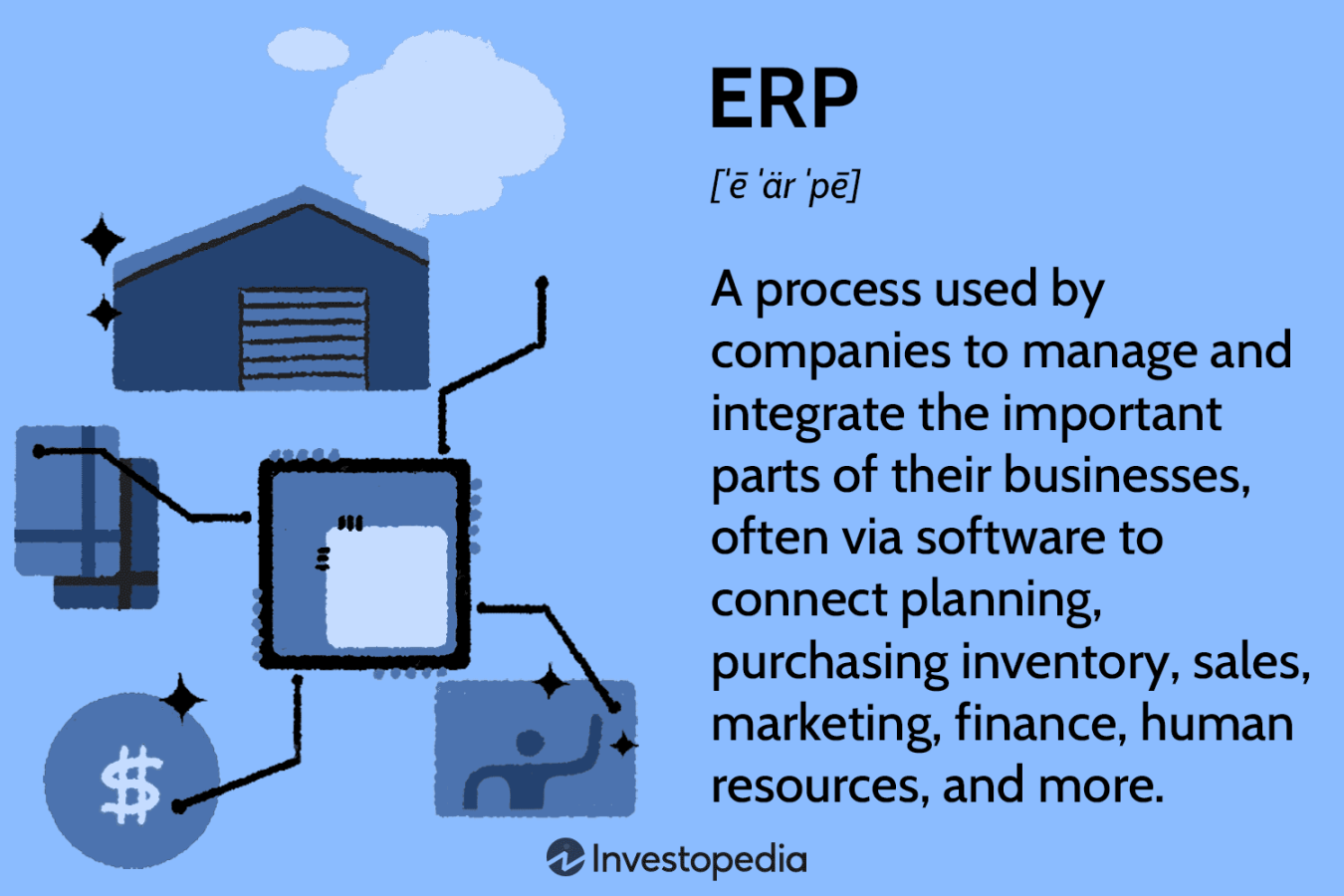
ERP systems offer a wide range of functionalities, catering to the specific needs of each department. Here’s a glimpse into some of the core functionalities:
Financial Management: ERP systems automate tasks like accounts payable and receivable, general ledger, budgeting, and financial reporting, providing real-time financial insights for informed decision-making.
- Supply Chain Management: ERP streamlines procurement, inventory management, and order fulfillment. It offers features like forecasting, demand planning, and warehouse management, ensuring optimal resource allocation and minimizing stockouts.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): ERP integrates customer data from sales, marketing, and support interactions, providing a 360-degree view of customer relationships. This enables targeted marketing campaigns, improved customer service, and enhanced loyalty.
- Human Resource Management (HRM): ERP automates HR processes like payroll, recruitment, performance management, and benefits administration. It facilitates employee self-service and streamlines talent management.
- Manufacturing: ERP optimizes production planning, scheduling, and material resource planning (MRP). It tracks production costs, monitors quality control, and ensures on-time delivery.
Benefits of Implementing an ERP System
The advantages of implementing an ERP system are numerous. Here are some of the key benefits:
Improved Efficiency and Productivity: ERP automates manual tasks, eliminates data silos, and fosters collaboration, leading to significant efficiency gains and increased productivity across departments.
- Enhanced Data Visibility and Accuracy: ERP provides a centralized platform for all business data, ensuring consistency and accuracy. Real-time data visibility empowers informed decision-making.
- Reduced Costs: Streamlined processes, optimized inventory management, and improved resource allocation lead to significant cost reductions. ERP also minimizes errors and rework, further enhancing financial performance.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Enhanced order fulfillment, efficient inventory management, and real-time data on customer interactions empower businesses to deliver exceptional customer service, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Better Decision-Making: ERP offers comprehensive business intelligence (BI) tools and reporting capabilities. Data-driven insights empower informed decision-making across all levels of the organization.
Different Types of ERP Systems
ERP systems come in various flavors to cater to the specific needs of different businesses. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
On-Premise ERP: This traditional approach involves installing and managing the ERP software on the company’s own servers. It offers greater control but requires significant upfront investment and IT expertise for maintenance.
- Cloud-Based ERP (Cloud ERP): Cloud ERP offers a subscription-based model where the software is hosted by a third-party provider. This eliminates the need for on-premise infrastructure and provides greater scalability and flexibility.